|
asr_ros_pkgs is a software framework which impements the approach 'Active Scene Recognition (ASR)' and has been developed at the Chair of Prof. Dr.-Ing. R. Dillmann, Humanoids and Intelligence Systems Lab (HIS), Karlsruhe Institute of Techology (KIT), Germany. ASR is an approach for mobile robots to recognize scenes in distributed and cluttered indoor environments. It combines scene recognition and object search: Information about partially recognized scenes is used to guide the subsequent search for missing objects. In implementing ASR, asr_ros_pkgs provides both |
- A scene classifier: A hierarchical data structure we introduce as 'Implicit Shape Model trees' together with learning and recognition algorithms.
- An integrated software architecture: A hierarchical state machine for ASR, including components for both scene recognition and object search.
The scene classifier can be used independently of ASR for what we call Passive Scene Recognition (PSR). As PSR, we define scene recognition with an immobile observer.
This project is of use for any researcher who intends to estimate the state of a robot's environment based on both the objects present in the environment and the 6-D spatial relations between the objects. Such estimates can be used for robotic decision-making, e.g., in the context of action planning.
As a starting point for
using our scene classifier without our object search (PSR), we recommend the tutorials in the package asr_ism
using ASR in order to control a mobile robot, we recommend the tutorials in the package asr_resources_for_active_scene_recognition
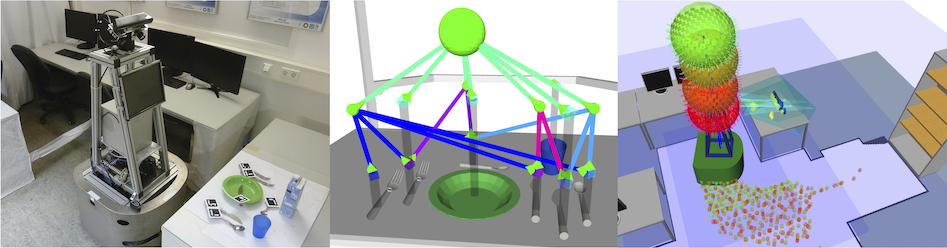
The research project 'Learning the Context in Programming by Demonstration of Manipulation Tasks', during the course of which asr_ros_pkgs was created, has been a 3-year research grant funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG).

The install instructions will guide you through the installation of ASR on Ubuntu 16.04 (and 18.04), click here.


- Active Scene Recognition consists of different packages, including both the functionalities Scene Recognition, Object Pose Prediction and Next-Best-View estimation, used by it as well as the logic (in a state machine) of Active Scene Recognition.

- The control package provides ROS access to actuators that both of our experimental setups (dome and robot) have in common. In particular, we provide a general-purpose ROS driver for FLIR pan-tilt-units.

- Packages which are related to the kinematic chain of the experimental setup „dome“ at our lab. This setup consists of a cage of aluminum profiles on which two actuated robot heads are mounted as well as of a magnet-tracking system "Flock of Birds“ and a pair of Cybergloves.

- This package contains all messages that are particular to our Active Scene Recognition system. These messages make up the interfaces between the different collaborating components of our software architecture.

- The robot package provides ROS access to navigation-related actuators and sensors, the kinematic chain and a gazebo simulation of our mobile robot (resp. our experimental environment „mobile robot). Moreover,, it provides a general-purpose local planner, following the „follow-the-carrot“ paradigm.

- The perception package wraps up low-level and high-level perception packages from RGB-D, laser and stereo-camera interfacing, over 6-DoF object localization to (passive) scene recognition. Passive scene recognition is performed with Implicit Shape Model trees, while 6-DoF object localization can be done by the help of fiducial markers or on the basis of the HALCON library.

- The utility package wraps up miscellaneous support functionalities, required by a variety of our packages.

- The results of the above-mentioned research project, achieved by the developed software framework, have so far been presented in the following publications:
P. Meißner and R. Dillmann. Implicit Shape Model Trees: Recognition of 3-D Indoor Scenes and Prediction of Object Poses for Mobile Robots. Robotics. MDPI, 12(6):158, 2023. [ videos ]
P. Meißner. Indoor Scene Recognition by 3-D Object Search for Robot Programming by Demonstration. Volume 135 of Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, 2020.
P. Meißner, R. Schleicher, R. Hutmacher, S. R. Schmidt-Rohr and R. Dillmann. Scene Recognition for Mobile Robots by Relational Object Search using Next-Best-View Estimates from Hierarchical Implicit Shape Models. In International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2016. [ video ]
P. Meißner, F. Hanselmann, R. Jäkel, S. R. Schmidt-Rohr and R. Dillmann. Automated selection of spatial object relations for modeling and recognizing indoor scenes with hierarchical implicit shape models. In International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2015. [ video ]
P. Meißner, R. Reckling, V. Wittenbeck, S. R. Schmidt-Rohr and R. Dillmann. Active scene recognition for programming by demonstration using next-best-view estimates from hierarchical implicit shape models. In International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2014. [ video ]
P. Meißner, R. Reckling, R. Jäkel, S. R. Schmidt-Rohr and R. Dillmann. Recognizing scenes with hierarchical implicit shape models based on spatial object relations for programming by demonstration. In International Conference on Advanced Robotics, 2013.
Further information on our research is available unter www.sceneexploration.org. We are happy to provide supplementary information and to improve this documentation. So please feel free to reach out to us through asr-ros AT lists DOT kit DOT edu if anything remains unclear after having read it.
When using Active Scene Recognition, please cite the 'Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics' book or our 'MDPI Robotics' article. Thank you!

